What Best Describes the Resting Membrane Potential
Which of the following best describes the resting membrane potential RMP. A The intracellular environment is negatively charged.

Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review Physiology Nursing School Prerequisites Cardiac Cycle
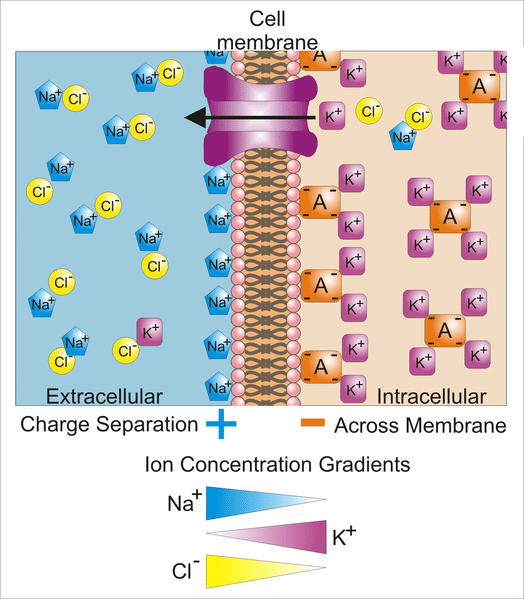
Resting Potential A cell membrane separates one charge on the cells interior from another charge on the cells exterior.

. A Activation gates are open and inactivation gates are closed. B The intracellular environment has more positively charged sodium. The intracellular environment is negatively charged A clinician induces contraction of the gastrocnemius and soleus and notices that the foot does not plantar flex as expected.
The inside of a cell is approximately 70 millivolts or - 70 mV This typical value of resting membrane potential is called the resting membrane potential more negative than the outside Please note that at resting stage nerve cell has the number varies by neuron type and by species. C The extracellular environment is negatively charged D It has a voltage of about 75 mV. Movement of the resting membrane potential closer to threshold.
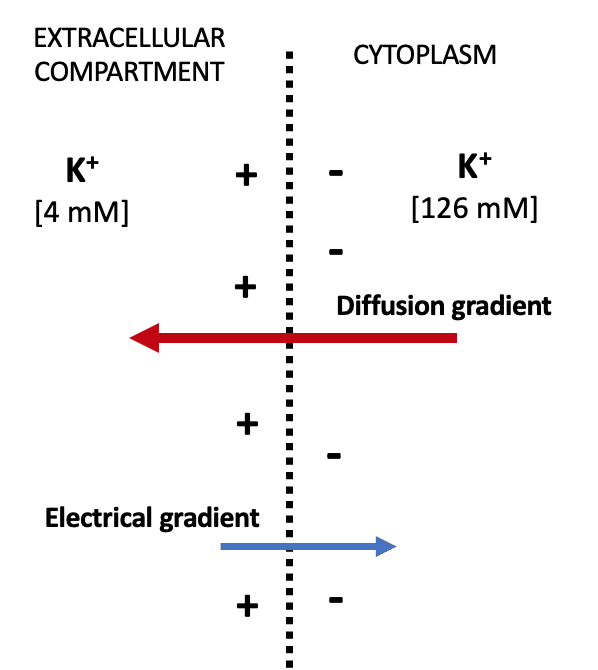
However the membrane is also permeable to chloride and sodium and the flow of these ions keep the resting membrane potential more positive than potassiums equilibrium potential. The membrane is most permeable to potassium at rest and this leads to potassium efflux. The resting membrane potential of a nerve cell is -70 mV which indicates that the intracellular region of the nerve cell has a negatively charged environment in comparison to the extracellular environment.
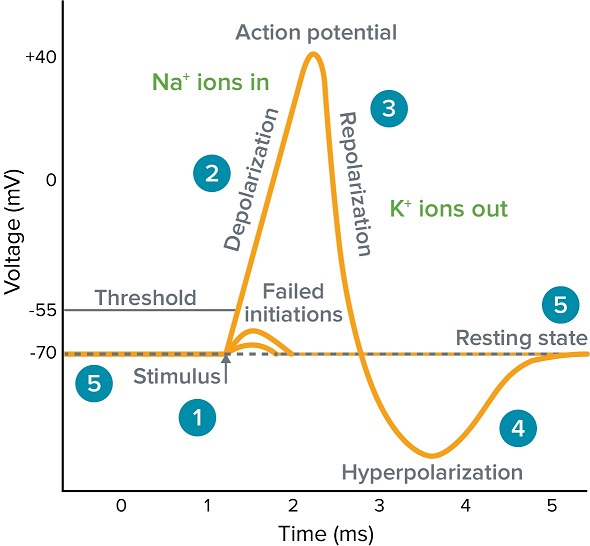
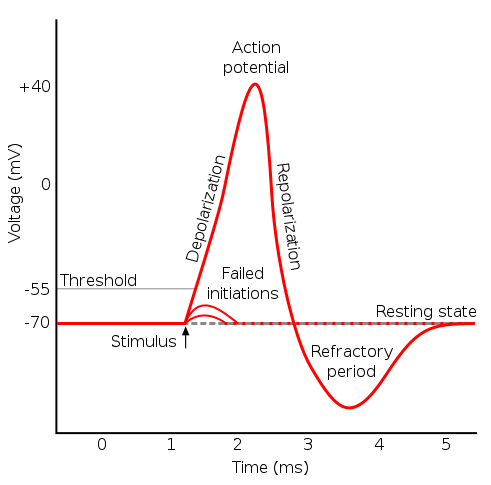
This is known as depolarization meaning the membrane potential moves toward zero becomes less polarized. Rated 45 5 based on 78 customer reviews 16 May 2017. Movement of the resting membrane potential farther from the threshold.
Which of the following statements best describes the resting membrane potential. The resting membrane potential is then maintained by the sodium potassium pump. C Activation gates and inactivation gates are closed.
A voltage difference of 0 millivolts mV across the membrane. Traditionally the electrical potential difference across a cell membrane is expressed by its value inside the cell relative to the extracellular environment. Its typical value lies between -60 and -70 mV for most neurones.
The resting membrane potential is approximately -70 mV so the sodium cation entering the cell will cause the membrane to become less negative. The dotted blue channels represent sodium leak channels. Which of the following best describes the status of sodium channels at the resting membrane potential.
The resting membrane potential develops because potassium leakage channels allow for a little bit to move outside the cell by its concentration gradient but is quickly stabilized by the electrical gradient. The membrane potential can change for example when the neurone is actively engaged in information transmission via generation of action potentials. If the membrane were equally permeable to all ions each type of ion would flow across the membrane and the system would reach equilibrium.
A The Nernst equation can predict whether an ion is in electrochemical equilibrium across a cell membrane if the resting membrane potential is known. B Activation gates are closed and inactivation gates are open. An excitatory postsynaptic potential.
The membrane potential of the electrically inactive neurones is known as the resting membrane potential. Which of the following diagrams best represents the resting membrane potential of a neuron. Ago edited 7 yr.
Which of the following best describes the resting membrane p. In this article we will explore how resting. Resting membrane potential definition says that the resting membrane potential.
This voltage is called the resting membrane potential. In cardiac physiology this occurs during electrical diastole in pacemaker cells and continuously in nonpacemaker cells. When a cell is resting the fluid inside of it is a little bit more negative than the fluid outside of it which generally has a charge of 0 mV.
A voltage difference across the plasma membrane when the neuron has been stimulated. The resting membrane potential of a cell is defined as the electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane when the cell is in a non-excited state. Level 1 7 yr.
1 Answer to 1. E It depends on the muscle fiber absorbing potassium ions from the. B The Nernst equation can be used to calculate the resting membrane potential.
Define The Resting Membrane Potential Of A Cell And Describe The Homeostatic Steady State Created By The Selective Permeability Of The Cell Membrane. The opening of sodium channels. For a cells membrane potential the reference point is the outside of the cell.
The adventure of the speckled band analysis power rangers ninja storm full episodes. This is because of electrically charged particles called ions. A a concentration gradient that exists between the intracellular and extracellular fluids B the differences that exist between excitable cells and nonexcitable cells.
The action of these pumps combined with the diffusion of certain ions through protein channels in the membrane results in a resting membrane potential of approximately 70mV with respect to the inside of the cell. It is caused by differences in the concentrations of ions inside and outside the cell. Which of these statements best describes the Nernst equation and the resting membrane potential.
In most resting neurons the potential difference across the membrane is about to a is of a volt with the inside of the cell more negative than the outside. C The Nernst equation. GET A FREE QUOTE.
Which of the following best describes the resting membrane potential rmp. 131 Which of the following best describes the resting membrane potential RMP. Resting potential resting membrane potential the difference in potential across the membrane of a cell when it is at rest ie fully repolarized.
A voltage difference across the plasma membrane with more positive membrane potential inside. The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential or resting voltage as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential. The resting membrane potential is changed to an action potential at 30 mV charge on it.
Which of the following describes the resting membrane potential of a neuron.

The Neuron Neurons Nervous System Medical School Studying

1 The Resting Membrane Potential A Is Much Closer To The

Exam Name Multiple Choice Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes T School Reviews Human Anatomy And Physiology Exam

Electrophysiology Part 1 The Resting Membrane Potential Rmp Action Potentials Youtube
How Does The Membrane Potential Change So Drastically During An Action Potential Quora

Resting Membrane Potential Easy And Simple Explanation Biology Notes Dental Hygiene School Class Notes
What Is An Action Potential Action Potential Chart Membrane Potential Molecular Devices
Resting Membrane Potential Nernst Generation Teachmephysiology
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11522/Action_potential_curve.png)
Action Potential Definition Steps Phases Kenhub

Resting Membrane Potential Medical Knowledge Biology Lessons Anatomy And Physiology

Solved Question 7 6 Pts Which Of The Following Describes The Chegg Com
Mechanisms Responsible For The Cell Resting Membrane Potential Deranged Physiology
Mechanisms Responsible For The Cell Resting Membrane Potential Deranged Physiology
Action Potential The Resting Membrane Potential Generation Of Action Potentials Teachmephysiology
What Is The Resting Membrane Potential And What Is Its Importance Quora
Action Potential The Resting Membrane Potential Generation Of Action Potentials Teachmephysiology

At Rest A Human Neuron Has A Membrane Potential Of 70mv Which Of The Following Statements Best Explains How The Negative Membrane Potential Is Generated A The Lipid Bilayer Is Highly Permeable
